1. Ore preparation
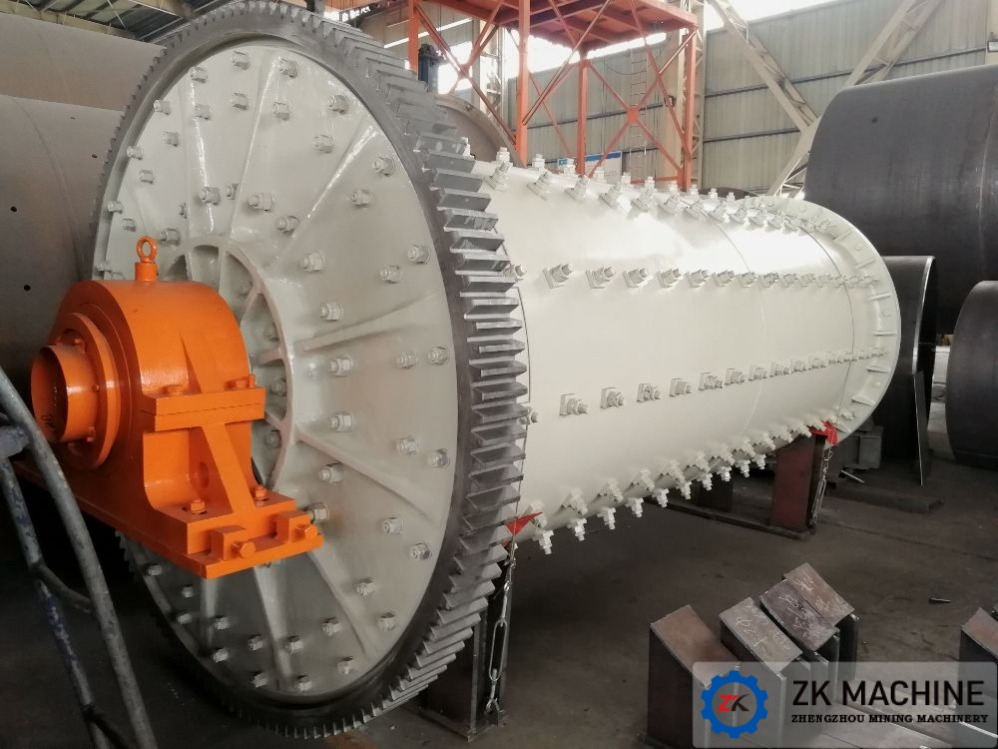
The first step in mineral processing is ore preparation. The mined ore is usually large in size and needs to be crushed and ground. First, the ore is crushed by a jaw crusher or a hammer crusher to crush the large ore into smaller particles (usually tens of millimeters). Then, the ore enters a fine crushing device (such as an impact crusher) for further crushing. The crushed ore is finely ground by a grinding device (such as a ball mill or a rod mill) to reduce the ore particle size to tens of microns for subsequent sorting.
2. Ore sorting
Gravity separation: The density difference between minerals and gangue is used to separate them through equipment such as jigs, shaking tables or spiral chutes. For example, gold mines often use gravity separation to recover coarse gold.
Flotation: For fine-grained copper or gold ores, flotation is the main method. By adding reagents, the target mineral is attached to the bubbles and floats, while the gangue sinks to the bottom.
Magnetic separation: Magnetic minerals such as iron ore can be separated by magnetic separators. Strong magnetic minerals (such as magnetite) are separated directly, while weak magnetic minerals (such as hematite) need to be treated by strong magnetic field equipment.
3. Concentrate treatment
Concentration: Remove excess water through a concentrator or cyclone to increase the concentrate concentration. Filtration: Use a filter to further dehydrate and obtain a concentrate filter cake. Drying: Use a dryer to remove the remaining water.
4. Tailings treatment
Tailings concentration: Reduce the water content of tailings through a concentrator or cyclone. Tailings discharge: Transport the tailings to a tailings pond or other treatment.
5. Product storage and transportation
After the concentrate is processed, it is stored in a warehouse or silo and then transported to a smelter or market by truck, train or conveyor belt.
6. Environmental protection and safety
Wastewater treatment: Treat mineral processing wastewater to ensure that it meets the discharge standards. Dust control: Use dust removal equipment to reduce dust pollution. Safety management: Regularly check the equipment to ensure safe operation.