The production process of micro-slag powder has two production processes: ball milling and vertical milling, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The ball milling system is a traditional slag grinding process. It has strong adaptability to materials, large specific surface area, better particle shape than vertical mills, simple maintenance and cheap accessories. However, it occupies a large area, consumes a lot of power, and needs to dry the materials separately, and the process is complicated. Vertical mill slag grinding is a system that has developed rapidly in recent years. The process is simple. Drying, grinding, and powder selection are all completed in the mill. The investment is low, the unit power consumption is low, and the heat transfer is fast, but the maintenance is more difficult than ball milling. In recent years, the comprehensive benefits of vertical mills in the cement industry due to the advantages of energy saving and consumption reduction have become more and more obvious, and they have also been widely used and promoted in the electric power, metallurgy, chemical, and non-metal industries.
1. Vertical mill production process
The slag is transported into the factory by truck and stored in the shed. The material is taken by a forklift, measured by a hopper and a quantitative feeder, and then directly sent to the vertical mill by a belt conveyor, and an iron remover is installed on the conveyor to remove iron.
The slag after iron removal enters the vertical grinding mill, and the slag powder after drying and grinding is collected by the bag filter and transported to the finished product warehouse by the air chute and elevator. The spit from the vertical mill is fed into the vertical mill again via the conveyor and elevator. The drying heat source is provided by a hot air stove.
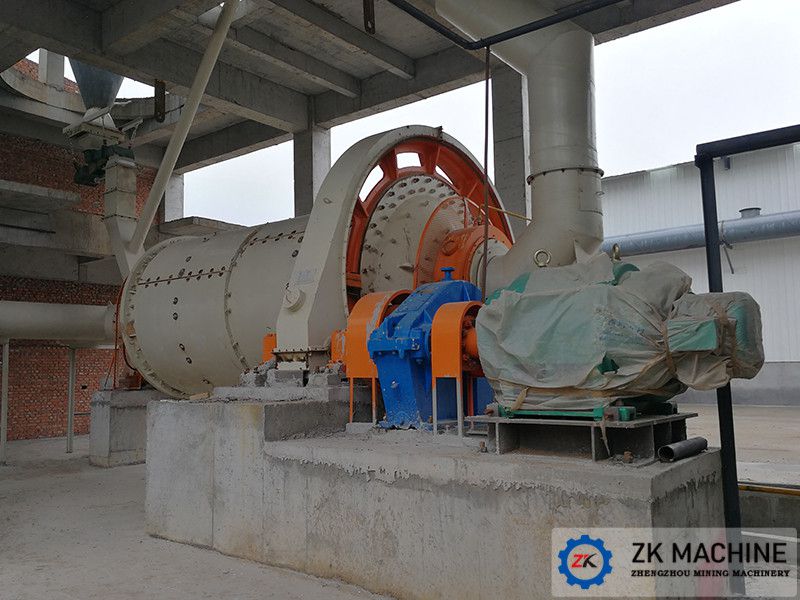
2. Ball mill production process
The slag is transported into the factory by truck and stored in the shed. The material is taken by a forklift, measured by a hopper and a quantitative feeder, and then sent to the dryer by a belt conveyor for drying. The dried slag enters the ball mill for grinding, and the ground slag is discharged from the bucket. The type hoist is sent to the powder concentrator for classification, and the qualified particle size is transported to the finished product warehouse by the air chute and hoist. Large-particle mineral powder is returned to the ball mill for re-grinding. The discharge end of the mill is equipped with a dust collector, and the fine powder collected by the dust collector is transported to the finished product warehouse by the air chute and elevator. The drying heat source is provided by a hot air stove.